
Tarangire National Park
Speak to our tour consultants for a more custom made itinerary to suit your travel needs.
Tel: +254 706 124 625
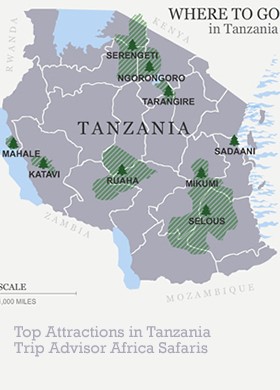
- Background Information
Tanzania’s Tarangire National Park is second only to Ngorongoro Conservation area in terms of concentrations of wildlife. The Park lies to the south of the large open grasslands of southern Maasailand and is named after the Tarangire River, which provides permanent water for wildlife in the Park. It is an easy drive by good tarmac road from Arusha, passing open plains and great views of Kilimanjaro and Mt Meru along the way. During the dry season the fierce sun sucks the moisture from the landscape, baking the earth a dusty red, the withered grass as brittle as straw. The Tarangire River has shrivelled to a shadow of its wet season self. But it is choked with wildlife. Thirsty nomads have wandered hundreds of parched kilometres knowing that here, always, there is water.
Tarangire boasts northern Tanzania’s biggest population of elephants, which can be seen crossing the grasslands in great herds at certain times of year. It is also distinctive for its stunning trees; magnificent baobabs, huge old acacias, which provide much needed shade for many animals, and the statuesque doum palms which rustle and clatter in the breezes. The most productive game driving is often along the banks of the river, where most of the mammals come down for their daily drink. Tarangire’s other draw is that although you are restricted to vehicles in the Park itself, its ecosystems extend over 10 times the size of the park boundary into a buffer zone. Here it is possible to walk and experience the very particular thrill of night game drives, when a whole new gambit of animal life (most with big eyes) is revealed. Herds of up to 300 elephants scratch the dry river bed for underground streams, while migratory wildebeest, zebra, buffalo, impala, gazelle, hartebeest and eland crowd the shrinking lagoons. It's the greatest concentration of wildlife outside the Serengeti ecosystem - a smorgasbord for predators - and the one place in Tanzania where dry-country antelope such as the stately fringe-eared oryx and peculiar long-necked gerenuk are regularly observed.
During the rainy season, the seasonal visitors scatter over a 20,000 sq km (12,500 sq miles) range until they exhaust the green plains and the river calls once more. But Tarangire's mobs of elephant are easily encountered, wet or dry. The swamps, tinged green year round, are the focus for 550 bird varieties, the most breeding species in one habitat anywhere in the world. On drier ground you find the Kori bustard, the heaviest flying bird; the stocking-thighed ostrich, the world's largest bird; and small parties of ground hornbills blustering like turkeys. More ardent bird-lovers might keep an eye open for screeching flocks of the dazzlingly colourful yellow-collared lovebird, and the somewhat drabber rufous-tailed weaver and ashy starling - all endemic to the dry savannah of north-central Tanzania. Disused termite mounds are often frequented by colonies of the endearing dwarf mongoose, and pairs of red-and-yellow barbet, which draw attention to themselves by their loud, clockwork-like duetting. Tarangire's pythons climb trees, as do its lions and leopards, lounging in the branches where the fruit of the sausage tree disguises the twitch of a tail.
::: Select Recommended Tours :::
-

Kilimanjaro Climb - 5Days Marangu
The Marangu route is one of the most popular routes to the summit of your Kilimanjaro Climb.
-

Zanzibar Luxury Beach Tour
Explore Zanzibar Beaches in style with exclusive access to top 5star properties in Zanzibar.
-

Kenya & Tanzania Adventure
Combine two of the best top Wildlife and Safari Destinations in East Africa - Kenya & Tanzania..